What is a UPS?
If you've arrived here, perhaps you still don't fully understand what a UPS is and how it works.
Well, we just have to explain it to you!
First, let's start with the very definition of UPS.
As you know these systems are usually called UPS. This acronym is nothing more than the acronym of the English term Uninterruptible Power Supply, which literally means "uninterrupted current source".
Already from the name we can therefore guess that it is equipment that compensates for the lack of current, supplying auxiliary power to the connected electrical devices.
In other words, the UPS allows you to keep your peripherals on when there is a blackout or a voltage surge, guaranteeing a certain autonomy and protecting the devices from potential damage deriving from a sudden shutdown.
All clear?
Well, now let's try to go into a little more detail.

How does a UPS work?
How is it that your TV won't turn off if the rest of the house is left in darkness?
Is it magic? Obviously not!
The UPS kicked in to protect your precious screen, and figuring out how it did it isn't as complicated as you might think.
You must know that each UPS is made up of three main elements:
Battery charger
A battery charger converts the voltage coming from your electricity grid, transforming it from alternating voltage (AC) into direct voltage (DC) and then charges the internal batteries.
Batteries
One or more batteries, in which the energy supplied by the battery charger is stored, to be used in the event of a power failure.
Inverter
An inverter, which in the event of a blackout draws energy from the batteries, reconverts it from direct voltage (DC) to alternating voltage (AC) and supplies it to the connected appliances.
Therefore, it is the internal batteries that continue to power your devices in the absence of a mains: the UPS is able to understand when a power cut occurs and intervene promptly, moving the power source from the mains to the batteries, with an almost instantaneous reaction time!
Generally speaking, this is the operating diagram of any UPS, even if there may be some variations depending on the type of UPS.
Follow us in the next chapter to find out what the different UPS technologies are and how they differ from each other.

Which are the different kind of UPS?
There are essentially three families of UPS on the market:
- Offline UPS
- Line Interactive UPS
- Online UPS
Depending on the specific needs, such as the environment of use, the peripherals that must be connected and the level of protection that is needed, the choice of the most suitable UPS could fall on a type or on a 'other.
Offline UPS
Also known as Standby UPS, Offline UPS are the UPS characterized by the simplest structure.
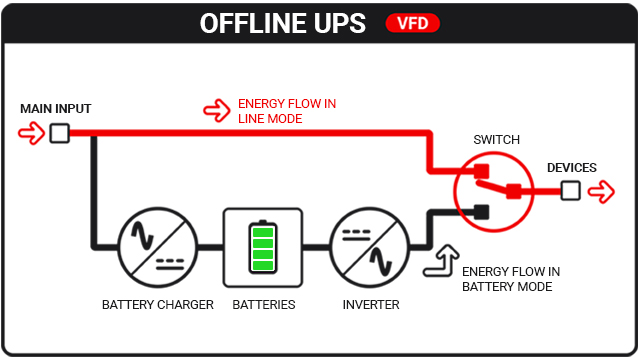
In normal operation (Line Mode) the devices connected to the UPS, defined as "load", are powered directly from the mains, without any transformation.
In the event of a mains failure, or when the input voltage goes outside the permitted tolerances due to a surge, the load is transferred to the inverter and consequently powered by absorbing energy from the batteries (Battery Mode).
The connected devices will therefore continue to operate until the battery charge is depleted or until the input power returns within the tolerances allowed by the UPS.
The intervention time is about 5-10 milliseconds.
Advantages
Offline UPSs are usually the cheapest.
Among the advantages of this solution there are also the compact dimensions, silence and excellent energy efficiency, as the battery charger is not constantly on.
Line Interactive UPS
Line Interactive UPSs are characterized by an architecture very similar to that of Offline UPSs, but they represent a sort of evolution thanks to the integration of an additional circuit called AVR (Automatic Voltage Regulator).
In the presence of slight voltage changes, this instrument automatically regulates and stabilizes the output voltage, bringing it back within the optimal threshold without having to switch to battery operation.
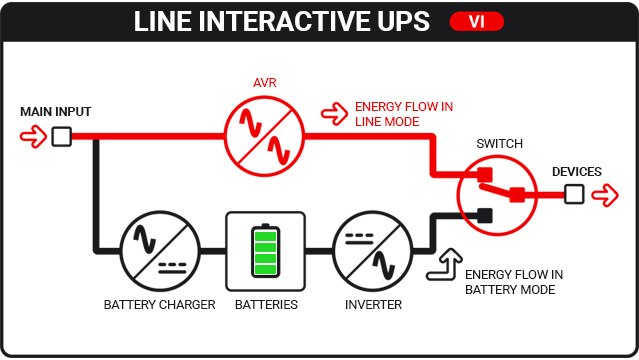
In normal operation (Line Mode) the load is powered by the mains through the AVR circuit, which constantly stabilizes the output voltage, bringing it back to the default values (about 230 Volts).
In the event of a mains failure, or when the power supply voltage does not fall within the tolerances allowed by the AVR circuit, the inverter intervenes which, through the energy accumulated by the batteries, guarantees the continuity of power supply to the connected load (Battery Mode).
The intervention time is about 5-10 milliseconds.
Advantages
Line Interactive UPSs are the most common type among non-professional users, above all thanks to the excellent quality/price ratio.
In fact, these models, despite being absolutely accessible from an economic point of view, offer a good level of protection to the connected devices thanks to the integrated voltage stabilizer function.
Then there are again a series of typical advantages of Offline UPS, such as, for example, ease of use, small size and high energy efficiency during mains operation.
Online UPS
Online UPSs are characterized by more advanced technology than the Offline and Line Interactive models, and guarantee absolute protection for connected devices.
This type of UPS is also called double conversion because it operates a double voltage conversion step (alternating/direct/alternating) in constant mode, even in the presence of incoming mains power.
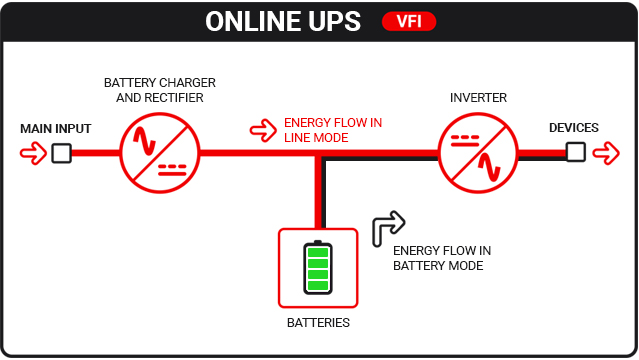
In normal operation (Line Mode), the input voltage undergoes an initial transformation, from AC to DC, through the Rectifier, and is then converted again, from DC to AC, through the Inverter, thus feeding the load. In the event of a mains failure, or significant voltage fluctuations, the rectifier is excluded from the circuit and the batteries continue to supply the load independently (Battery Mode).
The tripping time in this case is therefore almost nil.
Advantages
Online UPSs are a more important investment from an economic point of view, but currently represent the best technology available on the market, aimed above all at professional users.
Thanks to the double conversion process, the Online UPSs guarantee a completely regenerated current: the output power supply is perfect and independent from the input one, both in voltage and in frequency, and therefore of better quality than that coming from the common network electric.
The zero switching time and the ability to always generate a pure sinusoidal waveform in output are further advantages of this technology, guaranteeing maximum protection for the connected electronic devices.

And now, which one?
Now that you know how an Uninterruptible Power Supply works,
you just have to choose the one best suited to your needs.
If you need advice, our buying guide
is always at your disposal!




